Absolv Equations: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Solvation parameters/hydrogen bonding potential are essential characteristics of solutes that are key determinants of many biological properties. In certain cases a simple model relating the property of interest to solvation descriptors (Abraham type equation) may suffice for a quick estimate of the behavior of new compounds in the relevant system.<br> | Solvation parameters/hydrogen bonding potential are essential characteristics of solutes that are key determinants of many biological properties. In certain cases a simple model relating the property of interest to solvation descriptors (Abraham type equation) may suffice for a quick estimate of the behavior of new compounds in the relevant system.<br> | ||
The Absolv module is a product of cooperation between Pharma Algorithms and Prof. M. H. Abraham. Absolv Equations panel enables the user to calculate various solvent-solvent or gas-solvent partition coefficients from more than | The Absolv module is a product of cooperation between Pharma Algorithms and Prof. M. H. Abraham. Absolv Equations panel enables the user to calculate various solvent-solvent or gas-solvent partition coefficients from more than 250 predefined Abraham type equations may be calculated. Alternatively, any custom equations using predicted Abraham solvation parameters of a solute may be entered. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
# Select the equation’s category | # Select the equation’s category | ||
# Select an individual equation | # Select an individual equation | ||
# Edit a custom equation or view the preset one | # Edit a custom equation or view the preset one - opens the '''Edit Equation''' window (see below) | ||
# Create a new custom equation | # Create a new custom equation - opens the '''Edit Equation''' window (see below) | ||
# Delete the created equation | # Delete the created equation | ||
# Close the '''Equation Manager''' window | # Close the '''Equation Manager''' window | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
After the '''Edit...''' (3) or '''New...''' (4) button is clicked, the '''Edit Equation''' window appears: | |||
[[Image:Edit_Equation.png|center]] | [[Image:Edit_Equation.png|center]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<ol style="list-style-type:lower-latin"> | |||
<li> Enter the name of the equation</li> | |||
<li> Enter the value of the intercept</li> | |||
<li> Enter a coefficient of the corresponding solute property in the formula</li> | |||
<li> Choose between the available H-Bonding basicity parameters (B or Bo)</li> | |||
<li> Select the appropriate cavity effect and dispersion interactions descriptor (L or V)</li> | |||
<li> Select the category of the equation from the drop-down list or enter a name of the new one</li> | |||
<li> Enter comment</li> | |||
<li> Enter a literature reference</li> | |||
</ol> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Newly entered equations appear under the corresponding category in the Equation Manager and Equations pane: | Newly entered equations appear under the corresponding category in the '''Equation Manager''' and '''Equations''' pane: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 67: | Line 69: | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible | <div class="mw-collapsible"> | ||
==Technical information== | ==Technical information== | ||
| Line 75: | Line 77: | ||
===Calculated quantitative parameters=== | ===Calculated quantitative parameters=== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Absolv equations are commonly used to calculate the following groups of properties: | |||
* Water-solvent partitions | * Water-solvent partitions | ||
* Gas-solvent partitions | * Gas-solvent partitions | ||
| Line 81: | Line 83: | ||
General LFER equation relating solute properties (SP) to solvation parameters: | General LFER equation relating solute properties (SP) to solvation parameters: | ||
:SP = i + a·A + b·B (Bo) + e·E + s·S + v·V (l·L) | :SP = i + a·A + b·B (Bo) + e·E + s·S + v·V (l·L) | ||
The major difference between the equations for estimating water/solvent and gas/solvent partitioning coefficients is the choice of the parameter characterizing dispersion interactions and cavity effect. For the former group of properties McGowan characteristic volume (V) is used for this purpose, while for the latter group it is replaced by hexadecane/gaseous phase partitioning coefficient L. | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
===Reference database=== | ===Reference database=== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Absolv DB contains a browsable dataset consisting of 7885 compounds with experimental values of solvation parameters determined by Prof. M. H. Abraham and coworkers. The main literature references where the values comprising the Absolv DB were presented include: | |||
* Abraham, M. H., Grellier, P. L., Prior, D. V., Duce, P. P., Morris, J. J., and Taylor, P. J., ''J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans 2'', '''1989''', 699. | * Abraham, M. H., Grellier, P. L., Prior, D. V., Duce, P. P., Morris, J. J., and Taylor, P. J., ''J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans 2'', '''1989''', 699. | ||
* Abraham, M. H., Grellier, P. L., Prior, D. V., Morris, J. J., and Taylor, P. J., ''J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans 2'', '''1990''', 521. | * Abraham, M. H., Grellier, P. L., Prior, D. V., Morris, J. J., and Taylor, P. J., ''J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans 2'', '''1990''', 521. | ||
* Abraham, M. H., Whiting, G. S., Doherty, R. M., and Shuely, W. J., ''J. Chromatogr.'', '''1991''' (587), 213-228. | * Abraham, M. H., Whiting, G. S., Doherty, R. M., and Shuely, W. J., ''J. Chromatogr.'', '''1991''' (587), 213-228. | ||
<br /> | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:02, 8 August 2018
Overview
Solvation parameters/hydrogen bonding potential are essential characteristics of solutes that are key determinants of many biological properties. In certain cases a simple model relating the property of interest to solvation descriptors (Abraham type equation) may suffice for a quick estimate of the behavior of new compounds in the relevant system.
The Absolv module is a product of cooperation between Pharma Algorithms and Prof. M. H. Abraham. Absolv Equations panel enables the user to calculate various solvent-solvent or gas-solvent partition coefficients from more than 250 predefined Abraham type equations may be calculated. Alternatively, any custom equations using predicted Abraham solvation parameters of a solute may be entered.
Module interface

- Values calculated using selected equations
- Toggle the result of a corresponding equation invisible in the Results Pane
- All solvation equations are grouped according to their type. Switch between these groups by selecting an appropriate tab
- Name of a solvation property
- Equation used to calculate a particular property
- Comments on a corresponding equation
- Literature references
- Scroll through all available equations in the selected group
- Toggle the result of a corresponding equation visible/invisible in the Results pane
- Click to open the Equation Manager window
Equation Manager
Equation Manager allows defining new and editing or deleting the existing custom Abraham type equations as well as viewing all the predefined ones.
Note: The predefined internal equations can be neither altered nor deleted.

- Select the equation’s category
- Select an individual equation
- Edit a custom equation or view the preset one - opens the Edit Equation window (see below)
- Create a new custom equation - opens the Edit Equation window (see below)
- Delete the created equation
- Close the Equation Manager window
After the Edit... (3) or New... (4) button is clicked, the Edit Equation window appears:
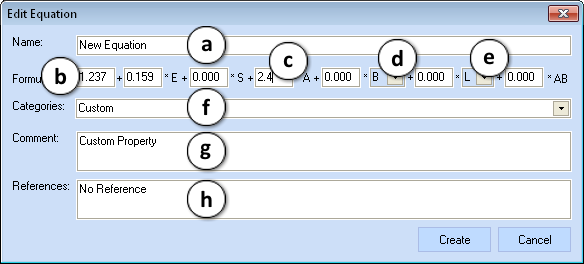
- Enter the name of the equation
- Enter the value of the intercept
- Enter a coefficient of the corresponding solute property in the formula
- Choose between the available H-Bonding basicity parameters (B or Bo)
- Select the appropriate cavity effect and dispersion interactions descriptor (L or V)
- Select the category of the equation from the drop-down list or enter a name of the new one
- Enter comment
- Enter a literature reference
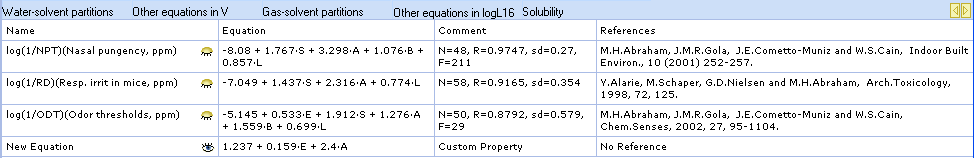
Newly entered equations appear under the corresponding category in the Equation Manager and Equations pane:

Technical information
Calculated quantitative parameters
Absolv equations are commonly used to calculate the following groups of properties:
- Water-solvent partitions
- Gas-solvent partitions
- Rough estimate of solute partitioning in biological systems (water-skin, water-cell permeation, etc.)
General LFER equation relating solute properties (SP) to solvation parameters:
- SP = i + a·A + b·B (Bo) + e·E + s·S + v·V (l·L)
The major difference between the equations for estimating water/solvent and gas/solvent partitioning coefficients is the choice of the parameter characterizing dispersion interactions and cavity effect. For the former group of properties McGowan characteristic volume (V) is used for this purpose, while for the latter group it is replaced by hexadecane/gaseous phase partitioning coefficient L.
Reference database
Absolv DB contains a browsable dataset consisting of 7885 compounds with experimental values of solvation parameters determined by Prof. M. H. Abraham and coworkers. The main literature references where the values comprising the Absolv DB were presented include:
- Abraham, M. H., Grellier, P. L., Prior, D. V., Duce, P. P., Morris, J. J., and Taylor, P. J., J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans 2, 1989, 699.
- Abraham, M. H., Grellier, P. L., Prior, D. V., Morris, J. J., and Taylor, P. J., J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans 2, 1990, 521.
- Abraham, M. H., Whiting, G. S., Doherty, R. M., and Shuely, W. J., J. Chromatogr., 1991 (587), 213-228.