Protein Binding: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible | <div class="mw-collapsible"> | ||
==Technical information== | ==Technical information== | ||
Revision as of 09:59, 15 June 2017
Overview
This module can be used to predict plasma protein bound fraction and the equilibrium binding constant to serum albumin of a compound. The binding properties are computed from lipophilicity and structural descriptors of the compounds. Reliability of each prediction is assessed by calculating corresponding Reliability Indices.
Features
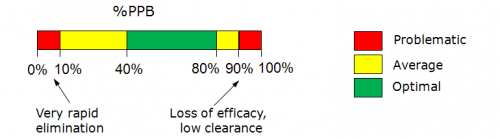
- Calculates %PPB – the cumulative percentage of the analyzed compound bound to human plasma proteins (such as albumin, alpha1-acid glycoprotein and others) and log KaHSA – human serum albumin affinity constants. with Reliability Index (RI) values of the corresponding predictions.
- RI values represent a quantitative evaluation of prediction confidence. High RI shows that the calculated value is likely to be accurate, while low RI indicates that no similar compounds with consistent data are present in the training set.
- Main plasma proteins that mostly contribute to binding of different compound classes in human plasma are enumerated in the textual comments next to the prediction results.
- Experimentally measured extent of plasma protein binding, human serum albumin affinity constants are displayed for up to 5 similar structures from the training set along with the corresponding literature references.
Interface
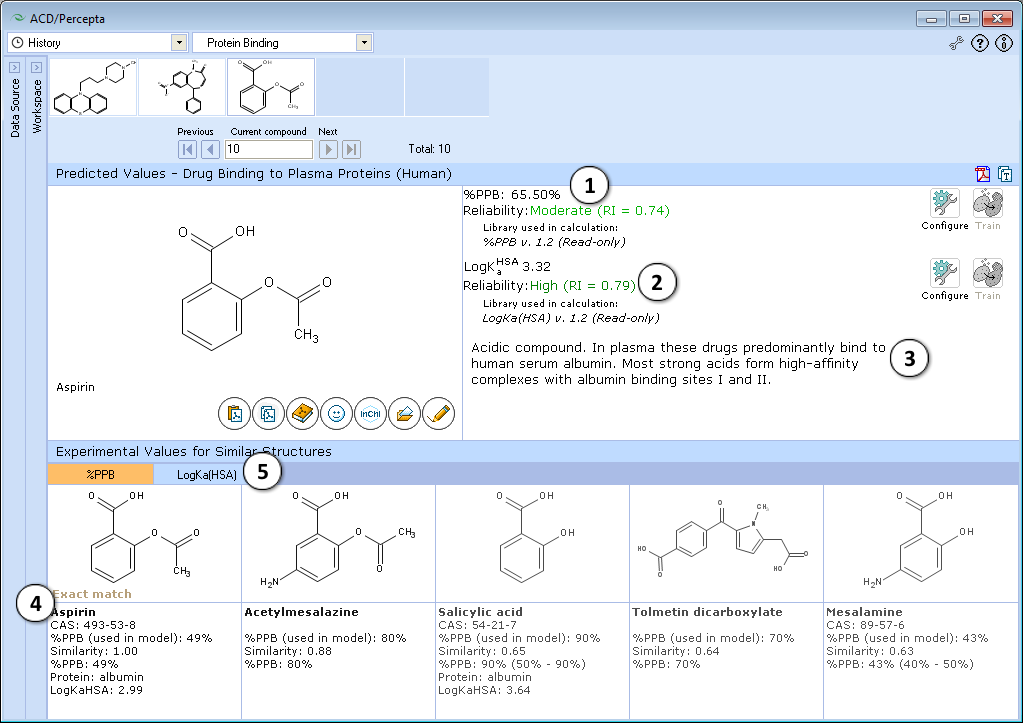
- Calculated plasma protein bound fraction and logarithm of the affinity constant to human serum albumin in the blood plasma:
- Reliability indices of predictions are provided along with the calculated values. Each of the properties also has dedicated "Configure" and "Train" buttons to select the training library for use in calculations and to add new data to that library. The name of the currently selected library is indicated with italic font.
- A brief general description of a compound’s likely binding behavior when dissolved in blood plasma, based on its physicochemical properties
- Up to 5 similar structures in the protein binding training set with experimental quantitative values of %PPB, LogKaHSA and literature references
- Switch between tabs displaying similar structures from %PPB and LogKaHSA databases
Note: Prediction reliability classification according to Reliability Index (RI) values:
- RI < 0.3 – Not Reliable,
- RI in range 0.3-0.5 – Bordeline Reliability,
- RI in range 0.5-0.75 – Moderate Reliability,
- RI >= 0.75 – High Reliability
Technical information
Calculated quantitative parameters
Parameters calculated by Distribution\Protein Binding module include percentage plasma protein binding values (%PPB) and log KaHSA constants. These properties are related, but characterize provide slightly different information about the considered process.
- log KaHSA represents the drug’s affinity constant to human serum albumin – the major carrier protein in plasma. Experimental data come from direct chromatographic determination of binding strength to that particular protein.
log KaHSA = log ([LA]/([L][A])) where [LA] is concentration of ligand bound to albumin, [L] – that of free ligand, and [A] – concentration of free albumin which is estimated at ~0.6 mM in human plasma.
- %PPB values represent the overall fraction of drug bound in human plasma, i.e. accounts for interactions with different proteins: albumin, alpha1-acid glycoprotein, lipoproteins, SHBG, transcortin etc. In vitro measurements of the extent of plasma protein binding usually involve equilibrium dialysis, ultrafiltration or ultracentrifugation methods.
%PPB = (1 – fu) * 100% where fu is fraction of free (unbound) drug in plasma ranging from 0 to 1.
- Supplementary Distribution\Vd module calculates apparent Volume of Distribution of drugs in human body expressed in liters per kg body weight (L/kg).
Experimental data
Experimental data that were utilized to build predictive models were collected from drug prescription information, reference pharmacokinetic tabulations and many original articles. The main sources of Vd data were well-known pharmacokinetic books: "Therapeutic Drugs" (ed. by C. dollery), and Goodman & Gilman's "The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics", while albumin affinity constants were collected mainly from original articles by Valko K. et al. J Pharm Sci. 2003;92(11):2236-48. [1], and Kratochwil N.A. et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;64(9):1355-74. [2] The compiled data sets contain %PPB data for almost 1500 compounds, about 340 albumin affinity constants and almost 800 Vd values.
Model development (technical details)
The predictive models of %PPB and log KaHSA were derived using GALAS (Global, Adjusted Locally According to Similarity) modeling methodology (please refer to [3] for more details).
Each GALAS model consists of two parts:
- Global (baseline) statistical model that reflects general trends in the variation of the property of interest.
- Similarity-based routine that performs local correction of baseline predictions taking into account the differences between baseline and experimental values for the most similar training set compounds.
GALAS methodology also provides the basis for estimating reliability of predictions by the means of calculated Reliability Index (RI) value that takes into account:
- Similarity of tested compound to the training set molecules.
- Consistence of experimental values and baseline model prediction for the most similar similar compounds from the training set.
Reliability Index ranges from 0 to 1 (0 corresponds to a completely unreliable, and 1 - a highly reliable prediction) and serves as an indication whether a submitted compound falls within the Model Applicability Domain. Compounds obtaining predictions RI < 0.3 are considered outside of the Applicability Domain of the model.
Both %PPB and log KaHSA are Trainable meaning that their Applicability Domains may be easily extended by addition of ‘in-house’ experimental data to the module Self-training Library. Notably, the baseline statistical model does not need to be rebuilt from scratch to account for data entered by the user. The model is retrained automatically as new compounds are added to the Library. Model trainability would be particularly useful for predicting serum albumin affinity constants as literature data sets are very sparse, thus the ability to take advantage of large ‘in-house’ libraries gives the potential for a significant improvement of both accuracy and reliability of calculations.