Aquatic Toxicity LC50
Overview
Aquatic toxicity module provides the researcher with an accurate and reliable predictive tool that may serve as a valuable first estimate of fish and daphnid toxicity of new chemical entities that is required under REACH. It may therefore be used as an initial screen that could compete and become at least a partial replacement of time and resource consuming experimental determination in animals.
Features
- A standard measure of aquatic toxicity is the concentration of the compound in water that is lethal to 50% of exposed organisms (LC50).
- Provides the predictive models of LC50 (mg/L) for two species that are typically used in aquatic toxicity assays: Fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) and Water flea (Daphnia magna).
- The calculated LC50 values are supported by reliability indices (RI) that provide an estimate of the prediction accuracy.
- RI values represent a quantitative evaluation of prediction confidence. High RI shows that the calculated value is likely to be accurate, while low RI indicates that no similar compounds with consistent data are present in the training set.
- The training sets used to build the models contain experimental data on aquatic toxicity for about 900 compounds in case of fathead minnows and about 600 compounds in case of water fleas.
Interface
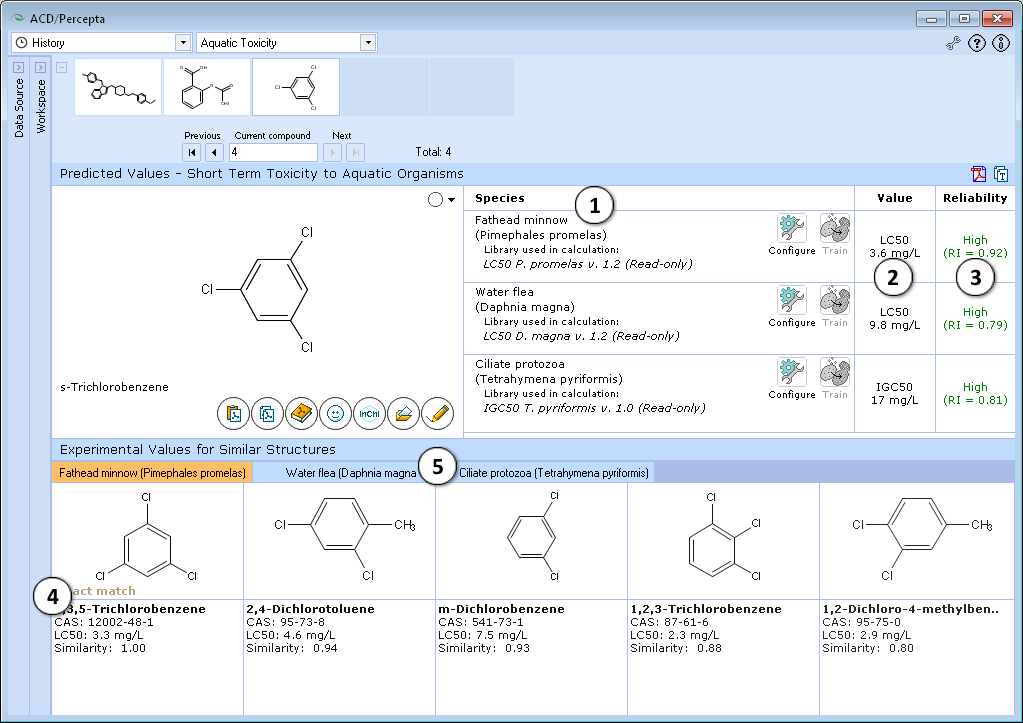
- Calculations performed by the predictive models are presented in the form of a table. Predictions are made for the two aquatic species most frequently used for testing - Fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) and Water fleas (Daphnia magna)
- The predicted value is LC50 of the analyzed compound for a given organism, expressed in mg/L.
- Predictions are supported by Reliability Index values ranging from 0 to 1 that serve as an intrinsic evaluation of prediction confidence:
- RI < 0.3 – Not Reliable,
- RI in range 0.3-0.5 – Bordeline Reliability,
- RI in range 0.5-0.75 – Moderate Reliability,
- RI >= 0.75 – High Reliability
- Up to five most similar compounds from the training set with names, CAS numbers and experimental LC50 values.
- Click the tab to browse the similar structures for different species. If no similar structures are found for a particular species, the corresponding tab is disabled.
Technical information
Calculated quantitative parameters
- Aquatic toxicity: standard measure of aquatic toxicity is the concentration of the compound in water that is lethal to 50% of exposed organisms (LC50). To obtain a linear relationship with structural properties these data were converted to logarithmic form (pLC50) for modeling, but the final prediction result is returned as an original LC50 value in mg/L.
- Endocrine disruption: In vitro measurement of estrogen receptor binding affinity (Log RBA) estimates the relative affinity of compound to receptor compared to reference ligand estradiol: %RBA = IC50(reference)/IC50(test compound) * 100%. Here IC50 is the concentration at which the unlabeled ligand displaces half of specifically bound radiolabeled 17β-estradiol to the ER, (reference estrogen in a typical experiment is the same 17β-estradiol). Experimental data were converted to binary representation with two cut-offs at Log RBA = -3, and Log RBA = 0. Predicted values are probabilities that tested compound will have Log RBA higher than the defined cut-offs. Based on the predictions compounds are classified as strong binders (Log RBA > 0), weak binders (Log RBA most probably falling in the range from -3 to 0), and non-binders (Log RBA < -3).
- Irritation: For modeling purposes experimental classification results of standard Draize test (not irritating, slightly irritating, irritating, etc.) have been transformed into a binary variable according to the following scheme: compounds producing at least moderate eye or skin irritation were considered positive and all the others - negative. The resulting probabilistic predictor estimates whether the analyzed compound is likely to act as as moderate or severe eye or skin irritant.
Experimental data
Experimental data that was used for the development of predictive models was collected from various reference databases (Aquatic toxicity - EPA, Endocrine disruption - FDA Endocrine Disruptors DB, Risk Assessment of Endocrine Disruptors (METI), Irritation - ECB-ESIS and RTECS), as well as original publications. After thorough verification of the obtained values the final data sets contained:
- About 900 compounds with quantitative LC50 values characterizing acute toxicity to fishes (Pimephales promelas), and about 600 compounds - to water fleas (Daphnia magna).
- Nearly 1500 compounds with experimentally measured ER alpha binding affinities.
- More than 2100 molecules in both eye and skin irritation data sets that include qualitative irritation categories determined after application of test compounds to adult albino rabbits.
Model features & prediction accuracy
The models for calculating LC50 of chemicals for aquatic organisms were developed according to the same methodology as Trainable Tox Boxes models (e.g. hERG Inhibition, Ames Genotoxicity, etc.) As a result, these models share the same advantage - possibility to obtain an intrinsic evaluation of prediction confidence by the means of Reliability Index (RI) values supporting each prediction. RI ranges from 0 to 1 and serves as an indication whether a submitted compound falls within the Model Applicability Domain:
- RI < 0.3 – Not Reliable - compound lies outside of the Model Applicability Domain
- RI between 0.3 and 0.5 – Borderline Reliability
- RI between 0.5 and 0.75 – Moderate Reliability
- RI >= 0.75 – High Reliability
The predictive models of Endocrine System Disruption and Irritation potential were built using binomial PLS method in Algorithm Builder. The models incorporated essential physicochemical properties of chemicals such as ionization and molecular size as well as fragmental descriptors including predefined substructures representing structural features known to have a profound influence on the analyzed property.
The resulting models are highly accurate:
- LC50 values for aquatic species are predicted with RMSE 0.5-0.6 log units when only predictions of moderate and high reliability (RI >= 0.5) are considered (RI values in the high and moderate ranges are provided for 30-60% of the validation sets).
- Overall accuracy of ER alpha affinity predictions exceeds 85% in both training and test sets in case of general binding model (Log RBA > -3), and exceeds 90% in case of strong binding (Log RBA > 0).
- Models for the prediction of rabbit eye and skin irritation produced overall accuracy of 78% and 73% respectively.