Acute Toxicity Categories
Overview
Acute Toxicity module performs rapid and accurate predictions of the tested compounds' LD50 values in rodents after various administration routes. In addition to the statistical model, ACD/Percepta contains a classification system that assigns the most likely OECD hazard categories (important for risk assessment) and an expert system that identifies structural elements typical for toxic compounds known from the literature.
Features
- All predictions are supported by Reliability Index (RI) values that represent a quantitative evaluation of prediction confidence. High RI shows that the calculated value is likely to be accurate, while low RI indicates that no similar compounds with consistent data are present in the training set.
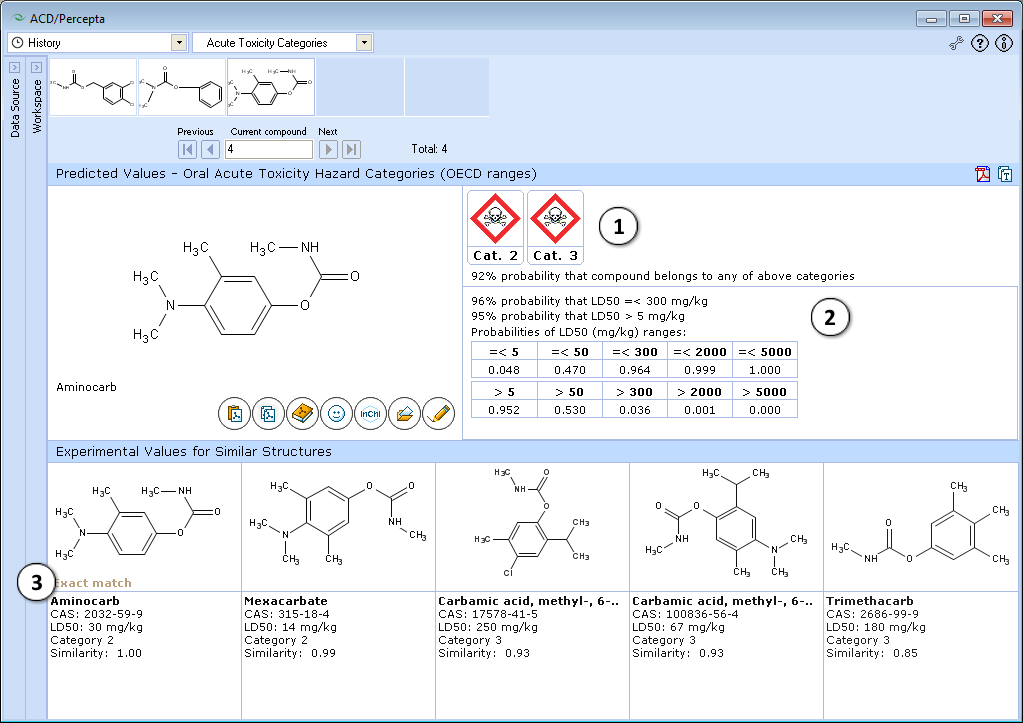
- Experimental LD50 value and similarity to test compound is shown for 5 most similar structures from the training set.
- Categories module defines possible “Oral Acute Toxicity Hazard Categories” for a compound and displays experimentally assigned categories for similar compounds.
- The chemicals are assigned to one of the five toxicity categories according to the numeric criteria expressed as LD50 (oral administration to rats). The categories were defined by OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. A Guide to The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS))
- Predictions are provided as a list of probabilities that the compound’s LD50 (rat, oral route) would exceed the cut-off values separating different categories. On the basis of these values, the software selects the most probable OECD Hazard categories for that compound
Interface
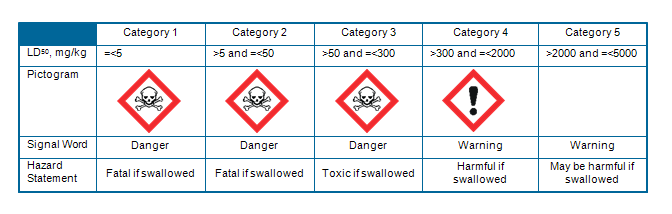
- Possible “Oral Acute Toxicity Hazard Categories” and corresponding oral acute toxicity labels. Chemicals can be allocated to one of five toxicity categories according to numeric criteria expressed as LD50 (oral administration to rats).
Hover over the label to see it more detailed: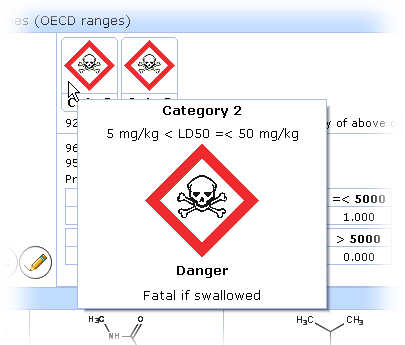
- Probability table describes the probability that LD50 value is lower (greater) than the defined limit. This table is the basis for the definition of oral hazard categories.
- Up to 5 similar structures from training set with experimental LD50 values (oral administration to rats), corresponding oral acute toxicity categories and similarity indices to tested compound are provided by the model.
Technical information
Calculated quantitative parameter
A standard measure of acute toxicity is LD50 (lethal dose 50) defined as a dose that is lethal to 50% of the treated animals. It can be viewed as a “cumulative potential” to cause various acute effects and death of animals. To obtain a linear relationship with structural properties these data were converted to logarithmic form (pLD50) for modeling, but the final prediction results returned to the user are converted back to LD50 value (mg/kg).
In ACD/Percepta LD50 is calculated for two different rodent species: toxicity for mice is estimated under oral, intraperitoneal, intravenous, subcutaneous administration, and for rats - under oral and intraperitoneal administration.
Model Features & Prediction Accuracy
Acute Toxicity predictor was built using critically evaluated experimental data for more than 100,000 compounds extracted from RTECS and ESIS databases.
The predictive models of LD50 for all considered species and administration routes were derived using GALAS (Global, Adjusted Locally According to Similarity) modeling methodology (please refer to [1] for more details).
Each GALAS model consists of two parts:
- Global (baseline) statistical model that reflects general trends in the variation of the property of interest.
- Similarity-based routine that performs local correction of baseline predictions taking into account the differences between baseline and experimental LD50 values for the most similar training set compounds.
GALAS methodology also provides the basis for estimating reliability of predictions by the means of calculated Reliability Index (RI) value that takes into account:
- Similarity of tested compound to the training set molecules.
- Consistence of experimental LD50 values and baseline model prediction for the most similar similar compounds from the training set.
Reliability Index ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 corresponds to a completely unreliable, and 1 - a highly reliable prediction. Compounds obtaining predictions RI < 0.3 are considered outside of the Applicability Domain of the model.
Predictive models of LD50 in various systems have been validated on external data sets. Validation results show that the accuracy of prediction is proportional to the Reliability Index. The predictions with a high or moderate Reliability Index (RI > 0.5) are accurate to RMSE of about 0.5-0.7 log units. Reliability Index values in this range were reported for 30-60% of compounds in the validation sets. More information regarding the modeling principles and validation results are available in our publication [2].
OECD Ranges
Chemicals are assigned to one of the five Oral Acute Toxicity Hazard Categories according to the numeric criteria expressed as LD50 (oral administration to rats). Categories were defined by OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. A Guide to The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS)):
- V – LD50 2000-5000 mg/kg (may be harmful if swallowed)
- IV – 300-2000 mg/kg (harmful if swallowed)
- III – 50-300 mg/kg (toxic if swallowed)
- II – 5-50 mg/kg (fatal if swallowed)
- I < 5 mg/kg (fatal if swallowed).
Toxicity hazards
Toxicity Hazards is a knowledge-based expert system that identifies and highlights structural elements that may be responsible high acute toxicity of compounds in rodents. Tox Hazards system contains a list of 86 predefined 'toxicophores' compiled after thorough analysis of toxicological literature. Significance of the defined hazardous fragments was verified on acute toxicity data set (more than 100,000 compounds).