P450 Inhibitors: Difference between revisions
Created page with "==Overview== <br /> Cytochrome P450 is the main enzyme family responsible for xenobiotic metabolism in human organism. Inhibition of these enzymes is among the main causes of..." |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Cytochrome P450 is the main enzyme family responsible for xenobiotic metabolism in human organism. Inhibition of these enzymes is among the main causes of possible drug-drug interactions responsible for a variety of undesirable adverse effects up to the lethal outcome. ACD/ | Cytochrome P450 is the main enzyme family responsible for xenobiotic metabolism in human organism. Inhibition of these enzymes is among the main causes of possible drug-drug interactions responsible for a variety of undesirable adverse effects up to the lethal outcome. ACD/Percepta predictive models for Cytochrome P450 Inhibition cover five major isoforms (3A4, 2D6, 1A2, 2C9, and 2C19) accounting for an absolute majority (>95%) of all biochemical transformations mediated by P450s. These models have been developed using datasets ranging from >4800 to nearly 8000 compounds and provide the probabilities that the compound of interest will inhibit a certain CYP450 isoform with IC<sub>50</sub> below one of the two selected thresholds. “General inhibition” models estimate whether the analyzed compound will exhibit any clinically significant CYP450 inhibition at all (IC<sub>50</sub> < 50 μM), while “Efficient inhibition” models predict probability that the compound will inhibit selected enzyme with IC<sub>50</sub> < 10 μM. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 10:28, 23 May 2012
Overview
Cytochrome P450 is the main enzyme family responsible for xenobiotic metabolism in human organism. Inhibition of these enzymes is among the main causes of possible drug-drug interactions responsible for a variety of undesirable adverse effects up to the lethal outcome. ACD/Percepta predictive models for Cytochrome P450 Inhibition cover five major isoforms (3A4, 2D6, 1A2, 2C9, and 2C19) accounting for an absolute majority (>95%) of all biochemical transformations mediated by P450s. These models have been developed using datasets ranging from >4800 to nearly 8000 compounds and provide the probabilities that the compound of interest will inhibit a certain CYP450 isoform with IC50 below one of the two selected thresholds. “General inhibition” models estimate whether the analyzed compound will exhibit any clinically significant CYP450 inhibition at all (IC50 < 50 μM), while “Efficient inhibition” models predict probability that the compound will inhibit selected enzyme with IC50 < 10 μM.
Features
- Predicts probabilities for a compound to exhibit either “General” (IC50 < 50 μM) or “Effective” (IC50 < 10 μM) Cytochrome P450 inhibition
- The quality of each prediction is evaluated by means of Reliability Index calculation
- Predictions are visualized in the form of a bar plot
- Classification based on the experimental data is presented for five most similar structures
- Allows the user to add experimental measurement data in order to expand the Applicability Domain of the Model
Interface
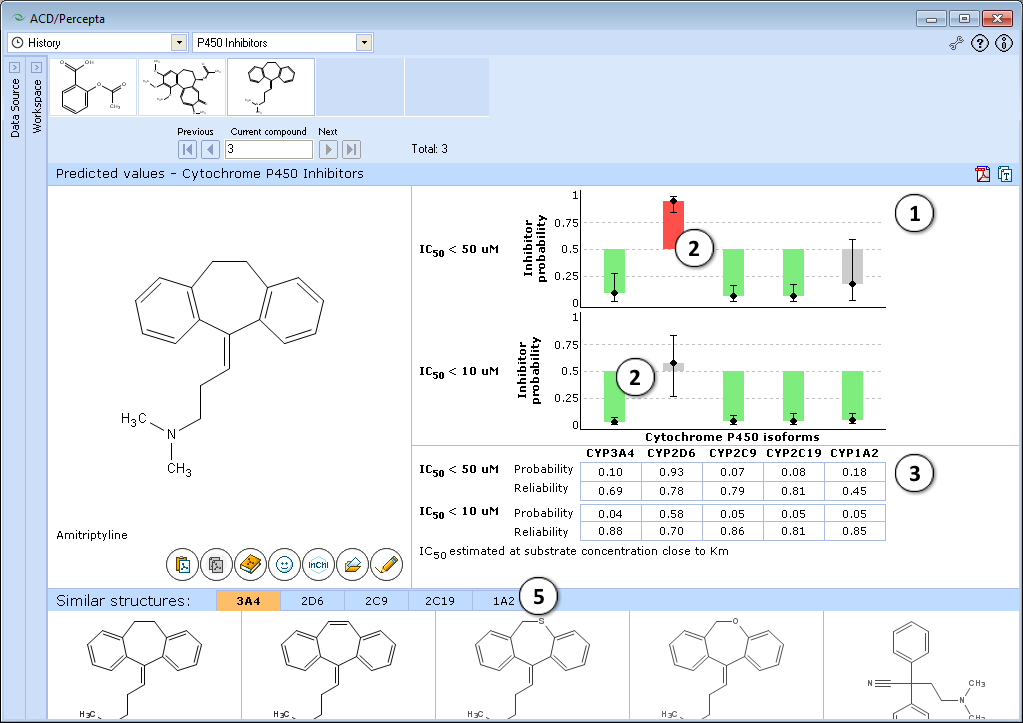
- Predictions are visualized in the form of bar plot. The upper part of the plot corresponds to the general inhibition model (IC50 < 50 μM), and the lower one – to effective inhibition model (IC50 < 10 μM)
- Height of the bar denotes estimated inhibitor probability, whiskers indicate prediction intervals. Red bars represent confidently predicted inhibitors, green bars – confident non-inhibitors, and gray bars – inconclusive predictions. The coloring scheme takes into account both predicted probability and the Reliability Index values
- The table below the chart shows exact values of calculated probabilities and Reliability Indices used to derive the bar plot
- Five most similar structures from the training sets are displayed with experimental data and literature references
- Click the corresponding tab to display similar structures for the relevant cytochrome P450 enzyme
Technical information
Predicted endpoints
CYP450 Specificity-related modules in ACD/ADME Suite provide the following quantitative predictions:
- P450 Substrates: Probability that the compound of interest will be metabolized by a certain CYP450 isoform.
- P450 Inhibitors: Probability that the compound of interest will inhibit a certain CYP450 enzyme with IC50 below defined threshold. Two types of predictive models utilizing different IC50 thresholds have been developed. "General inhibition" models estimate whether the analyzed compound will exhibit any clinically significant CYP450 inhibition at all (IC50 < 50 μM), while "Efficient inhibition" models predict probability that the compound will inhibit selected enzyme with IC50 < 10 μM.
- P450 Regioselectivity: Probability to be metabolized in human liver microsomes (or by a specific CYP450 enzyme) for every atom in the molecule.
Predictions are provided for five major cytochrome P450 isoforms (3A4, 2D6, 2C9, 2C19, 1A2) that are responsible for more than 80% of Phase I metabolism. In addition to Regioselectivity models for individual enzymes, overall HLM Regioselectivity module is also available. This module estimates the overall probabilities of human liver microsomal metabolism taking place at particular sites of the molecule. All predictions are supplied with Reliability Indices (RI) serving as an internal measure of prediction confidence (see Model Features section for more details about RI calculation).
Sources of experimental data
- P450 Metabolism (Substrate specificity and metabolism sites): only experimental data from original scientific publications were used for modeling of cytochrome P450 metabolism sites. The full dataset contained ~700 compounds with >800 possible metabolism sites. The literature dataset was expanded with information about marketed drugs’ metabolism and the expanded dataset was used for cytochrome P450 substrate modeling.
- P450 Inhibition: Two types of experimental data were used for cytochrome P450 inhibition modeling, including data from original scientific publications, information about marketed drugs, as well as data from the NCBI PubChem project.
Data sets
The sizes of the data sets used to develop the predictive models of substrate and inhibitor specificity are presented in the table below:
| Isoform | N (Substrate specificity) | N (Inhibitor specificity, cut-off: IC50 < 50 μM) | N (Efficient inhibition, cut-off: IC50 < 10 μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYP1A2 | 935 | 4867 | 5815 |
| CYP2C9 | 867 | 7666 | 7677 |
| CYP2C19 | 794 | 6899 | 6833 |
| CYP2D6 | 1001 | 7707 | 7507 |
| CYP3A4 | 960 | 6684 | 7927 |
Regioselectivity models were based on experimental data for 873 compounds collected from publications dealing with analytical identification of the metabolites observed after the incubation of compound with human liver microsomes or recombinant cytochrome P450 enzymes. Every carbon atom with at least one hydrogen attached was marked as a site of metabolism, if hydroxylation at the atom was observed, or site of no metabolism otherwise. For dealkylation reactions, carbon atoms of the leaving groups were marked in the same manner. Some sites were marked as "inconclusive" and consequently not used in the modeling. The table below shows the overall number of marked atoms used for building the models:
| No. of atoms | HLM | CYP3A4 | CYP2D6 | CYP2C9 | CYP2C19 | CYP1A2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | 1269 | 795 | 354 | 288 | 249 | 383 |
| Inconclusive | 340 | 176 | 49 | 43 | 15 | 61 |
| Negative | 7182 | 6757 | 6305 | 6314 | 5210 | 6020 |
| Total | 8791 | 7728 | 6708 | 6645 | 5474 | 6464 |
Fully searchable CYP450 Specificity databases are not available in the current version of ACD/ADME Suite, yet each prediction performed by P450 Substrates and Inhibitors modules is displayed along with experimental data for five compounds from the training set most similar to the molecule of interest. The provided information for similar compounds includes classification as substrates/non-substrates (inhibitors/non-inhibitors at two IC50 cut-offs) of the relevant CYP450 enzyme assigned on the basis of experimental results together with original references. In case of Regioselectivity predictions five most similar atoms from the training set are shown with color-marks indicating whether a metabolic reaction taking place at the particular site of the molecules was observed experimentally.
Model features & prediction accuracy
The model was developed with Algorithm Builder using a novel methodology consisting of two parts:
- Global baseline statistical model employing binomial PLS with multiple bootstrapping using a predefined set of fragmental descriptors.
- Local correction to baseline prediction based on analysis of experimental data for similar compounds.
The underlying methodology enables obtaining an intrinsic evaluation of prediction confidence by the means of Reliability Index (RI) values calculated for each prediction. RI ranging from 0 to 1 serves as an indication whether a submitted compound falls within the Model Applicability Domain. Two criteria influence the calculation of Reliability Index of a prediction:
- Similarity of the analyzed molecule to compounds in the Self-training Library (prediction is unreliable if no similar compounds have been found in the Library).
- Consistency of experimental data for similar compounds (discrepant data for similar molecules lead to lower RI values).
The predictive models of CYP450 substrate and inhibitor specificity are also Trainable meaning that their Applicability Domains may be expanded to account for the ‘in-house’ experimental data available in your company without the need to rebuild the baseline statistical model from scratch. Addition of new compounds to the module Self-training Library results in an instant improvement of prediction accuracy for the respective compound classes. Moreover, addition of 'in-house' data allows adapting the existing model to the particular experimental protocol used in your company and avoiding potential issues related to discrepancies between different experimental methods used for determination of drug interactions with CYP450 enzymes.
If the compound is within model Applicability Domain (acceptable reliability index) accuracy and sensitivity of classification is close to 90% for inhibitors and close to 80% for substrates. The accuracy of in silico prediction of cytochrome P450 inhibitors is comparable to the screening results. Metabolism sites are predicted correctly if there are similar metabolism sites in the dataset and if the reliability of prediction (RI value) is high.